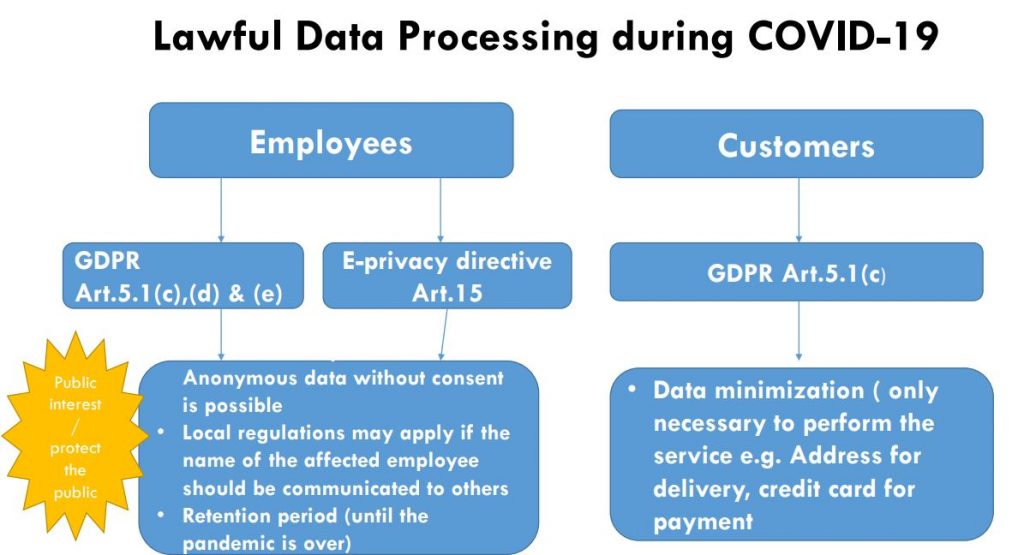
The worst scenario would be when a digital retailer is struggling to survive after COVID-19, only be served
with legal summon over data privacy violations. During this period, the European Data Protection
Regulatory Board issued a statement on data processing during COVID-19 which I have summarized in the
figure below.
- Article 5.1(d) and (e) can be referred to process data relating to employees who may have contracted
the virus without their consent in order to protect the data subject and others from the same and to
provide information to relevant authorities to help to fight the pandemic as long as the minimum
necessary information is provided and the privacy and dignity of the data subject are observed.
- Mobile location data may be used to monitor, contain or mitigate the spread of COVID-19. This would
imply, for instance, the possibility to geolocate individuals or to send public health messages to
individuals in a specific area by phone or text message. Public authorities should first seek to process
location data in an anonymous way (ie. processing data aggregated in a way that individuals cannot be
re-identified), which could enable generating reports on the concentration of mobile devices at a certain
location (“cartography”). Personal data protection rules do not apply to data which has been
appropriately anonymised. When it is not possible to only process anonymous data, the ePrivacy
Directive enables Member States to introduce legislative measures to safeguard public security (eprivacy directive Art. 15).